Biological function of hair - protective. Hair on the head, prevent it from overheating and protect it in cold weather, as well as from mechanical impact (impact). Eyelashes protect eyes from foreign bodies (dust, dirt), and hair in nostrils and ears intercept foreign bodies and prevent them from getting inside the body. Eyebrows protect your eyes from sweat.

Hair structure
Approximate composition of healthy hair:
The main chemical elements in the hair are:
- carbon (49.6%)
- oxygen (23.2%)
- nitrogen (16.8%)
- hydrogen (6.4%)
- sulfur (4%)
- in microscopic quantities: magnesium, arsenic, iron, phosphorus, chromium, copper, zinc, manganese, gold.
Hair consists of two enlarged parts:

- Kernel - the outer, visible part of the hair, protruding above the surface of the skin.
Hair shaft
The outer (visible) part of the hair - the rodconsists mainly of the horny protein substance - creatine.
Blood does not enter the hair shaft, there are no nerve endings. Therefore, when you cut, we do not feel pain, hair does not bleed.

The hair shaft consists of:
- cuticle - the outer part of the rod, consisting of 6-9 overlapping layers of cells of transparent amorphous keratin, resembling in scale structure (as in fish or pine cones). The space between the scales is filled with lipid layers (fatty acids), due to which the scales fit snugly together. Scales are directed from the root of the hair to its tip.
Cuticle function mainly protective, which protects the cells of the inner layer of the hair shaft (cortex) from exposure to water, sun and mechanical stress.
When exposed to hair alkaline environment (ordinary soap) cuticle flakes open, when exposed to acidic - closed. This property is important to consider when cosmetic procedures.
Main function of cortex - it is giving the hair shape, preserving the elasticity and strength of the hair.
Due to the peculiarities in the structure of this layer, people can have straight or curly hair, which in turn is genetically inherited.
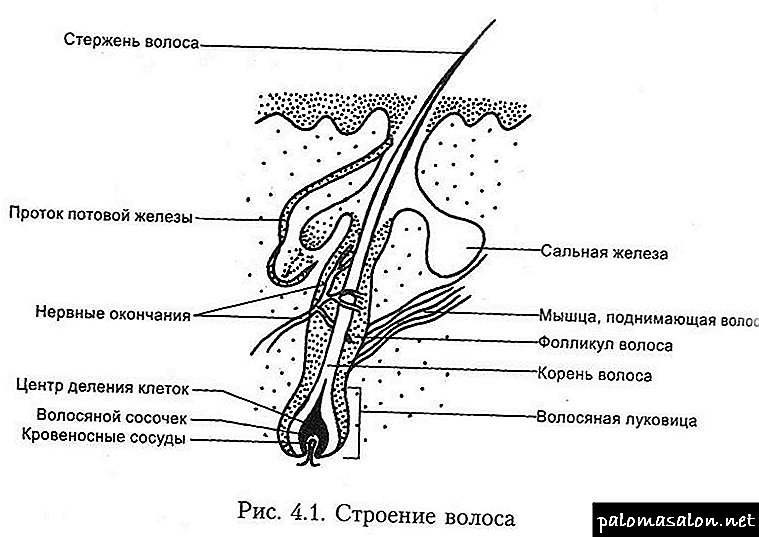
Hair Root (Hair Follicle)

The subcutaneous part of the hair (root or follicle) consists of:
- root sheath (external epithelial vagina)
- inner root sheath (internal epithelial vagina)
- bulb (hair papilla)
- sebaceous gland
- hair lifting muscle
Man is born with already formed follicles and each person has this number individually and is inherited from parents at the genetic level.
In addition, the number of hair follicles is different in people with different hair color. On average, the total amount of hair on the head:
- blondes - 140 thousand
- brown-haired - 109 thousand.
- brunette - 102 thousand
- red - 88 thousand
Hair begins to grow in the hair follicles.
The rate of cell division of the hair follicle takes second place in the human body after the rate of cell division in the bone marrow. Due to this, hair grows about 1–2 centimeters per month.
Hair color
Among the scales are the cuticle, and among the cores of the cortex layer, pigment granules in the form of melanos are located, which give the hair a certain color. Hair tint is determined by genetic factors and depends on the ratio of the contents of the two main pigments: eumelanin (black hair) and pheomelanin (Red hair).
In this way, hair color depends on a combination of two factors: the ratio of pigments and the number of pigment cells in the hair structure.
Hair types
The condition of the hair itself depends on the intensity of the sebaceous glands of the scalp. The higher the sebum secretion by the glands, the higher the fat content of the hair itself. Sebum spreads over the entire surface of the hair, covering them with a thin film. Depending on the "fatness" of the hair, they are divided into four types:
- greasy hair (increased hair greasiness)
- differ in the increased shine
- stick together in separate strands
- elastic
- more thick
- pollute quickly and lose their appeal
- cause difficulties when doing hairstyles
- don't electrify
- dry hair (reduced hair greasiness)
- have a dull look
- difficult to comb and tangle
- split on tips
- strongly electrify
- normal hair (normal functioning of the sebaceous glands)
- moderate, healthy hair shine
- obedient when combing
- flexible and elastic
- no split ends
- don't electrify
- mixed hair (greasy roots and dry split ends)
- hair looks dull and lifeless
- fatty at the roots
- brittle, starting from the middle of the hair length
- tips split
- poorly electrified
Interesting hair facts:
- hair roots begin to form at the end of the third month of fetal development
- on the head, the hair does not grow evenly - on the crown more densely, and on the temples and forehead less often
- in an adult on the head on average about 100 thousand hairs
- hair grows on average in three days by 1 mm (i.e. per month by 1 cm)
- in summer and during sleep, hair grows faster
- rate of hair loss - from 60 to 120 pieces per day. In place of falling out begin to grow new hair, from the same hair follicles.
How hair grows
 That part of the hair that grows out from under the skin of a person consists of dead tissue. The hair growth cycle continues for several years. After the old hair falls out, the new cycle begins again.
That part of the hair that grows out from under the skin of a person consists of dead tissue. The hair growth cycle continues for several years. After the old hair falls out, the new cycle begins again.
The process of hair growth is divided into three stages. Onfirst stage hair grows actively.Second stagegrowth is called intermediate: at this time the hair no longer grows, but the cells of the papilla are still functioning. Onthird stage hair growth completely stops. The functioning of the hair is arranged so that, under the influence of the growth of a new hair, the old one falls out, after which the new hair again runs through all the cycles.
The first stage of hair growth can last 2-4 years, the second - about 20 days, the third - up to 120 days. If we evaluate all the hairs of a person as a whole at a certain point, then approximately 93% of hairs are in the first phase of growth, 1% of hairs experience the second phase of growth and 6% of hairs - the third. Hair on the head and body can repeat growth cycles for a person’s life 24-25 times.
Hair grows all over, except for the soles and palms. An adult has about 100,000 hairs on his body. The amount of hair depends on what color they are. So, most of the hair on the body of the blonde.
Hair begins to appear in a person in the third month of fetal development. On the body, there is uneven hair growth. The hair on the eyebrows grows most slowly, their fastest growth is observed on the head. For three days, the hair on your head can grow by 1 mm. Normally, a person can lose 50-100 hairs per day. Normal hair loss is a physiological process. Fastest hair grows in a man in summer and spring.
Hair properties
 Each hair contains 97% protein (keratin) and 3% moisture. Keratin - This is a proteinaceous substance, which includes sulfur, vitamins, trace elements. Defined several types of hair that grow on the body. Long hair is the most durable and grows on the head, as well as those are the hair of the beard, mustache, genitals, underarms.
Each hair contains 97% protein (keratin) and 3% moisture. Keratin - This is a proteinaceous substance, which includes sulfur, vitamins, trace elements. Defined several types of hair that grow on the body. Long hair is the most durable and grows on the head, as well as those are the hair of the beard, mustache, genitals, underarms.
Bristly hair is hair growing in the nose and ears, as well as eyebrows and eyelashes. Bulk hair grows on the skin of the arms, legs, torso, face.
Healthy hair is elastic and has a high margin of safety. Healthy hair is easily stretched and can withstand up to 200 g load. Human hair is hygroscopic: it easily absorbs moisture. They are resistant to acids, but react very poorly to alkalis.
Most hair is located on the vault of the human skull. Eyebrows on average contain about 600 hairs, and eyelashes - about 400.
If the functioning of the hair is determined by their properties, then the color depends on how the two types correspond. melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. These types of melanin are distinguished by the shape of the granules: in eumelanin, the granules are elongated, and the shape of the granules of pheomelanin is oval or round. Therefore, eumelanin is called granulated pigment, and pheomelanin is called diffuse. All hair contains two types of pigments in different ratios. Consequently, people have three different hair colors: red, blond and brunette. But the shades of hair color is much more: there are up to 300.
Hair functions
 The function of the hair is very important for a person. First of all, hair is an ornament, that is, they perform an aesthetic function. They can both emphasize the dignity of a person, and hide his flaws. However, not only aesthetic functions are performed by human hair. They help to avoid both hypothermia and overheating of the head. An air layer is created in the hair that helps to keep both heat and cold. Fluffy hair, which is located on the body, participate in the processes of touch. Hair that grows in the ears and nose helps to trap dust. Human eyelashes help protect the eyes. Those armpit hairs can reduce friction. Consequently, a person makes any movements, and the skin is not damaged. In addition, some substances may accumulate in the hair. This is their function successfully used by criminologists in the process.
The function of the hair is very important for a person. First of all, hair is an ornament, that is, they perform an aesthetic function. They can both emphasize the dignity of a person, and hide his flaws. However, not only aesthetic functions are performed by human hair. They help to avoid both hypothermia and overheating of the head. An air layer is created in the hair that helps to keep both heat and cold. Fluffy hair, which is located on the body, participate in the processes of touch. Hair that grows in the ears and nose helps to trap dust. Human eyelashes help protect the eyes. Those armpit hairs can reduce friction. Consequently, a person makes any movements, and the skin is not damaged. In addition, some substances may accumulate in the hair. This is their function successfully used by criminologists in the process.
In general, the functions of hair in mammals are reduced to providing insulation, protecting the skin from external influences, and ensuring coloring (in animals it is a matter of disguise and attractiveness). In addition, animals have special hair that allows them to navigate in the open space, that is, they are responsible for sensitivity. But in the process of evolution, human hair has partially lost such functions.
As our hair grows
The average head is decorated with about 130,000 hairs. On average, one hair on our head lives 2-5 years. At the same time, blondes have more hair than brunettes, and red hair has less of them all.

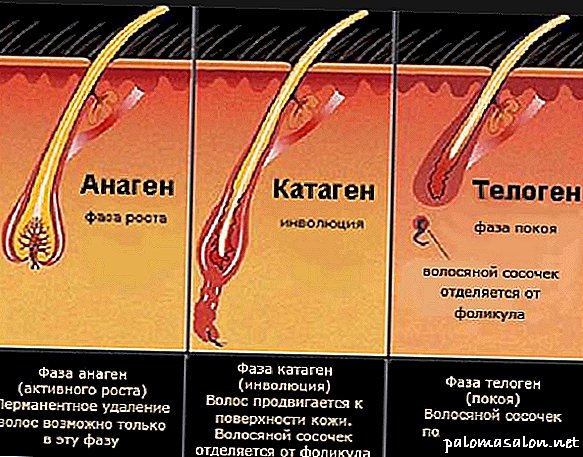
Hair growth occurs due to cell division in the hair follicle and includes three stages:
- Anagen (growth phase) - the period of the most active growth, during which keratin is actively produced - the main building substance for the hair. This period lasts from 2 to 5 years. The duration of the phase determines the maximum length of the hair. First, the follicle produces thin hair fiber (fluff hair), then the hair becomes thicker and pigmented (terminal).
- Catagen (follicle degradation phase) is a transitional period from the stage of active growth to the stage of rest. During this period, the hair follicle is separated from the hair papilla, therefore, the food is broken, the hair growth stops. Phase lasts several weeks.
- Telogen (rest phase) - a period in which the hair is separated from the root and slowly moves to the surface of the skin. Duration 2-4 months. During this period, the restoration of the connection between the hair follicle and the hair papilla occurs, after which the life cycle of the hair again passes into the growth phase.
Each hair follicle is programmed to produce 25-27 hairs, i.e. on the passage of 25-27 cycles. With each change of cycle, the papilla rises somewhat upward, and the hair rises higher with it. With age, the life cycles of the hair are reduced, strands become thinner, lose pigment and elasticity.
Every person is born with a genetically incorporated number of hair follicles that cannot be changed. Each follicle has its own muscles and innervation (connection with the central nervous system).
Any follicle is an independent formation, each hair has an individual structure, it develops and grows. That is why the process of updating the curls occurs unnoticed.
The growth and development of the hair follicle may undergo changes due to physical, chemical exposure from the outside, or in the presence of certain chronic diseases of the internal organs or the scalp.
The total number of follicles is individual. For example, in brunettes, hair is at least 100,000 hairs, and in blondes, over 150,000.
Normally, according to various data, 85% of hair follicles are in the growth phase (anagen), 1% are in the degradation phase (catagen) and 14% are in the rest phase (telogen).
Every day we lose 50-80 telogenic hair with the help of hats and hairbrushes. This is absolutely normal. With the loss of 100 or more hair per day, we are already talking about intensive prolapse, which requires treatment.
On our site you can take a test to determine the condition of your hair, and find out if you need cosmetic assistance.
Curl Color
Trichologists distinguish more than 50 shades of strands, but 8 colors are considered the most common:
- Ashen,
- Light brown
- Dark brown-haired,
- Blonde
- Light chestnut
- Dark chestnut
- The black.
A certain shade of hair is due to the amount of melanin in the structure of the coloring pigment, a proteinaceous formation that contains nitrogen, sulfur, arsenic and oxygen.
Hair damage
Regardless of the structure of the hair and their structure, under the influence of a number of negative factors. Experts identify three main types of core defects:
- Kinks due to mechanical damage
- Hair fragility on the background of irregular shapes,
- Twisting hair due to congenital abnormalities.
Fortunately, you can always restore the hair structure. The main thing is to notice the problem in time and begin treatment.
ALERANA® shampoo is perfect for dyed curls of all. The active ingredients of the shampoo enhance blood microcirculation in the hair follicles, stimulate the growth of curls, restores the hair structure, improves the nutrition of the strands, and protects the color from tarnishing.
Understanding Hair and Scalp
Every person's entire body is covered with the smallest hairs. The only exceptions are flexion surfaces, lips, lateral surfaces of fingers, nail phalanges, palms and feet. In some places the hair is barely noticeable, in others it grows only in a certain color.
Before considering the structure of the hair, you need to understand what functions their nutrient medium, that is, the skin.
The structure of the scalp
The skin covers the entire body of a person, it is about 5% of body weight. On the head, this organ consists of several layers, which, in turn, are further subdivided into more subtle formations.

1. Epidermis (the upper layer consists of partially dead cells that are removed during the washing process):
2. Dermis (the upper layer with blood vessels and nerve endings). It contains the well-known protein collagen, giving the skin elasticity and smoothness.
3. Hypodermis (hypodermic cellulose). Its main function is to provide thermoregulation.
The cells of the basal layer of the epidermis have two renewal periods during the day: in the morning and in the afternoon, up to 15 hours. At this time, cortisol levels are low. This period is considered the most favorable for the care of the scalp and the whole body.
Scalp functions
1. Protective. Sebum protects the body from harmful microorganisms. Epidermis prevents mechanical damage.
2. Immune. T lymphocytes detect endogenous and exogenous antigens. Largengans cells transport alien bodies to the lymph nodes in which they are neutralized.
3. Receptor. The ability of the skin to perceive and recognize tactile and temperature stimuli.
4. Exchange. The skin breathes, and also secretes through the sebaceous and sweat glands, secrets that create a thin film on its surface.
5. Thermostatic. During the temperature increase outside the skin vessels dilate, which increases heat transfer. A significant decrease in temperature makes it necessary to slow down the blood flow and thereby reduce evaporation.

After studying the structure and functions of the scalp, it becomes clear that for normal hair growth you must also have a healthy foundation that holds them. It can be powered in two ways: internal and external. Given that the outer layer of the skin consists mainly of dead cells that no longer need food, it becomes important to supply it from the inside with vitamins and minerals. To do this, you need to eat right, and if necessary, additionally take natural vitamin complexes.
Human hair structure
Hair is a horn formation of the skin. They are present only in humans and mammals. Filamentous formations cover part of the surface of the head.
You can study the structure of the hair under a microscope. It should be borne in mind that, considering the scalp, you can not just see. Under it is hidden a very important part - the root. Therefore, considering the structure of the hair, you need to study their internal and external components. Read about it below.
Hair growth stages
1. Anagen (2-4 years). At this time, there is the greatest activity of the follicle, as there is an intense division and growth of cells. Due to this hair is constantly growing. In some cases, this stage lasts up to 5 years. In a healthy person, about 85-90% of hair is of that age.
2. Catagen (15-20 days). At this stage, the follicle activity is reduced, but the papilla cells are still weakly functioning. By the end of the period, the bulb is torn away from the feeding papilla. Only 1% of hair is in this phase.
3. Telogen (90-120 days). During this time, the cells in the hair root no longer divide, and the hair bulb leaves its place along with the stem.

After this, the anagen phase of the new follicle begins on the free space formed.
Features of growth are still in the angle under which the rod grows. The structure of the scalp and hair in the aggregate may issue a tube at an angle from 10 to 90 °. That is why some women simply cannot afford to make themselves volumetric styling. This means that most of their hair grows at an angle of 10-20 ° and simply can not fit in the opposite direction.
A similar problem in men appears in the inflamed areas on the face. They have ingrown hairs that could not rise above the surface of the skin.
The structure of the hair on the head is slightly different from their counterparts in other places on the body. For example, they are able to withstand a load of up to 200 grams, this indicates their strength. About the flexibility of the possibility of hair styling in all sorts of hairstyles
Scalp
Scalp skin can cause hair problems. So, excessive production of sebum by it leads to the fact that the strands quickly get dirty, stick together, seem stale. Its insufficient production, on the contrary, leaves the curls defenseless against the influence of the environment, because they do not create a protective film.
The skin has three main layers:
- Epidermis (external),
- Derma (medium)
- Subcutaneous fatty tissue (lowermost layer).
This structure has skin tissue anywhere on the body. The cells of the epidermis are dead, you remove them during combing and washing. The appearance of dandruff is associated with such removal of skin scales. The epidermis also consists of brilliant, basal, granular and horny layers.
Interesting fact: the cells of the basal layer of the epidermis are updated twice - early in the morning and in the afternoon, before 15 - 00. During this period any care will be the most effective.
The dermis is the main dermal layer. It contains nerve endings and blood vessels, capillaries. It contains collagen - a pledge of elasticity of the skin and its youth. In the dermis there are sebaceous glands, hair bags pass through it and the epidermis. The hypodermis or subcutaneous fatty tissue "deals" with the body's thermoregulation.

The composition of the hair on the human head
The composition of the human hair is not too complex. It can not be called living tissue. Nevertheless, it grows due to active cell division in the zone of its base. However, the rod that is visible to us does not have nerve endings, is not supplied with blood and, like nails, is a static "dead" formation.
The main component in the composition is keratin, that is, a protein formed by amino acid compounds, such as cystine and methionine. Sulfur atoms are also contained. Protein (keratin) in healthy hair, which has not been subjected to thermal, chemical treatment or dyeing, contains about 80% or slightly less. About 15% water, 5-6% linid and 1 or less pigment percentage.
But the composition of the hair can vary. This occurs under the influence of several factors:
- Taking some drugs
- Perform certain medical procedures and procedures.
- Coloring, brightening, toning the hair,
- Frequent and intensive heat treatments (blow-drying, straightening, curling, etc.),
- Chemical treatments, both positive and negative (masks, balsams, perm / straightening),
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol),
- Eating Disorders, Diet,
- Changes in metabolism.
The normal chemical composition of the hair - an important rule of competent care for hair. Only such strands are responsive to treatment and do not cause problems for their owner.

The secret of hair structure
Know the structure of the hair is important for the implementation of competent care. This will help to choose the right products for care, to properly comb and lay the strands, to be more careful with the strands, etc.
It was said above that at their base, hidden in the skin, each hair has a “living” zone, from which growth occurs. In this zone, active cell division and the generation of new hair occur. The rate of cell division there is very high. The zone is located in the deep layers of the dermis, in fact, on the border with the hypoderm, at the very bottom of the hair sac.
This zone is called the follicle. It can not be damaged, since it is she who is most important when growing. The follicle is fed by blood from the blood vessels, which can also be considered part of the hair. In addition, there are other parts:
- Root,
- The papilla of the hair follicle,
- The muscle of the hair (they are responsible for the appearance of "goose bumps" while reducing them),
- The sebaceous gland produces sebum and is responsible for protecting the hair and scalp.
All these organs are located in the dermis. Through the epidermis passes only the rod itself. This is his visible part. The core is partially located in the skin and its maximum part, outside it.
The follicle is an important part of the scalp
The structure of the hair root (its follicle) is complex. In fact, this is the entire part of the hair, which is responsible for its growth and is under the skin. The synonym is the hair bulb. Since this area is alive, the person is in pain when removed "by the root." With such a regular removal, the root is damaged, and the hair stops growing at all.
Hair papilla is a large education responsible for the growth and life of the hair. When removed, if it survived, it will soon grow a new hair. If the papilla was damaged, it will no longer recover. It is permeated with blood vessels and nourishes the hair with essential substances.
The hair muscle is attached to the follicle just below the sebaceous gland. It is reduced under the influence of psychological factors and in the cold. As a result, "goose bumps" and "hair stand on end." The sebaceous gland itself is not part of the hair. But it is necessary for its normal development.

Like the nails, the hair has a protective cuticle. It is located on the rod and is its outer layer. Quite a thick layer (comparable to the thickness of the hair). Consists of 5 - 10 layers of cells. They are horny, large, have an elongated shape and a lamellar character. They are called “hair scales”.
They are located similarly to the tile, because damage to even one such plate leads to unpleasant processes in the entire rod. They overlap each other in the direction from the roots to the tips, because the ends should be kept very carefully.
Performs a protective function. It depends on her smoothness, brilliance and appearance. The function of balsams, masks, etc. means - closing scales and, thereby, the restoration of maximum protection. While shampoo, by contrast, reveals them for maximum cleansing.

Cortex - sturdy rod
Cortex is the core of the rod. The thickness of a human hair depends on the volume of this part. Cortex makes up 85% of the entire hair. Whereas the remaining 15% are divided between the medulla and the cuticle. Cortex consists of pure keratin protein. In one hair of a small length of such keratin fibers there may be tens of thousands.
Collagen fibers are successively intertwined, forming chains. These chains, intertwining among themselves, form directly the hair shaft.
It is in this part that most chemical processes occur. Coloring pigment. The change of color takes place in the cortex. The pigment penetrates the cuticle scales, opened with paint, to the hair's own pigment and changes it. Similarly, there are other chemical processes in this part of the hair.

The structure of the hair on the head has a medulla. This is the central part. It is located under the layers of the cuticle and cortex. Not every kind of hair on a human body has this part. Gun hair and some other types on the body are deprived of this part of the cortex and cuticle. This part has nothing to do with physical properties or structure. In fact, it is not needed. Responsible only for thermal conductivity strands. Chemical processes in it are also absent.
It consists of medulla. Inside it are microscopic air bubbles, which are heated (or cooled). Due to them thermal conductivity, temperature change, etc. are achieved.

Phases of growth with a pattern
Growth comes in three phases. Moreover, hair types and their structure do not affect the presence of these phases or their duration. Throughout life, each hair passes through three stages cyclically and repeatedly:
- Anagen - growth. Lasts 2 - 6 years. The older the person, the shorter this phase (i.e., growth retardation). At this stage, cells divide rapidly,
- Catagen - transitional period to the third stage. On it, the nipple begins to gradually atrophy. Blood supply is reduced, and then disappears. Growth does not occur. The hair bulb loses nutrition, the cells become horny. Catagen lasts 2 - weeks,
- Telogen is a short stage. Hair does not grow and does not develop, it is a stage of "rest." At this stage fall out. If a person has an increased loss, this stage comes too soon. After the removal of the telogen hair, a new anagen stage begins to grow.
The structure of the hair does not change. Thus, for the life of a person, each follicle is able to reproduce about 10 hairs.
4 elements of the structure of the hair on the human head: the main thing
The structure of a human hair is its main characteristic, based on the knowledge of which the development of means for the care and treatment of curls is carried out. When a hair's structure is broken, problems appear, such as dullness, breakage, etc. Restoring this structure is the goal that all actions of professional and folk remedies for hair are directed to.

The follicle is an important part of the scalp
The structure of the hair root (its follicle) is complex. In fact, this is the entire part of the hair, which is responsible for its growth and is under the skin. The synonym is the hair bulb. Since this area is alive, the person is in pain when removed "by the root." With such a regular removal, the root is damaged, and the hair stops growing at all.
Hair papilla is a large education responsible for the growth and life of the hair. When removed, if it survived, it will soon grow a new hair. If the papilla was damaged, it will no longer recover. It is permeated with blood vessels and nourishes the hair with essential substances.
The hair muscle is attached to the follicle just below the sebaceous gland. It is reduced under the influence of psychological factors and in the cold. As a result, "goose bumps" and "hair stand on end." The sebaceous gland itself is not part of the hair. But it is necessary for its normal development.

Like the nails, the hair has a protective cuticle. It is located on the rod and is its outer layer. Quite a thick layer (comparable to the thickness of the hair). Consists of 5 - 10 layers of cells. They are horny, large, have an elongated shape and a lamellar character. They are called “hair scales”.
They are located similarly to the tile, because damage to even one such plate leads to unpleasant processes in the entire rod. They overlap each other in the direction from the roots to the tips, because the ends should be kept very carefully.
Performs a protective function. It depends on her smoothness, brilliance and appearance. The function of balsams, masks, etc. means - closing scales and, thereby, the restoration of maximum protection. While shampoo, by contrast, reveals them for maximum cleansing.
 Cut hair under the microscope
Cut hair under the microscope
Cortex - sturdy rod
Cortex is the core of the rod. The thickness of a human hair depends on the volume of this part. Cortex makes up 85% of the entire hair. Whereas the remaining 15% are divided between the medulla and the cuticle. Cortex consists of pure keratin protein. In one hair of a small length of such keratin fibers there may be tens of thousands.
Collagen fibers are successively intertwined, forming chains. These chains, intertwining among themselves, form directly the hair shaft.
It is in this part that most chemical processes occur. Coloring pigment. The change of color takes place in the cortex. The pigment penetrates the cuticle scales, opened with paint, to the hair's own pigment and changes it. Similarly, there are other chemical processes in this part of the hair.

The structure of the hair on the head has a medulla. This is the central part. It is located under the layers of the cuticle and cortex. Not every kind of hair on a human body has this part. Gun hair and some other types on the body are deprived of this part of the cortex and cuticle. This part has nothing to do with physical properties or structure. In fact, it is not needed. Responsible only for thermal conductivity strands. Chemical processes in it are also absent.
It consists of medulla. Inside it are microscopic air bubbles, which are heated (or cooled). Due to them thermal conductivity, temperature change, etc. are achieved.
 Medulla in the center of the hair
Medulla in the center of the hair
The thickness of the hair and their number
The structure of the human hair on the head is to some extent determined by their color.The thickness of the rod is about 100 microns in red, 75 microns in brunettes, and 50 microns in blondes.
The number of rods on the head of different people is 100-150 thousand. This is genetically determined.
The shape of the hair, that is, the presence or absence of curls or just waves, is determined by the peculiarities of the follicle location relative to the surface of the head.

Thus, having studied the structure of human skin and hair, it becomes clear how to care for them, nourish, style and at what time it is desirable to do it.
The structure of human hair: known and not very facts and information
Hair is an important component of a person’s appearance. We are proud of them, when they are beautiful and thick, we are upset if they split or fall out, we make a huge amount of hairstyles of them, trying to make our appearance as attractive as possible. But what do we know about them? How do they work, what do they eat, how do they live and grow? But the structure of the hair is a complex system with its own special structure, life cycle and needs. Have you ever thought that if we knew more about our hair, perhaps we would be more careful and attentive to them, and they would always please us with the shine of thick hair?
What are they
Hair is one of the elements of the protective cover of the body. Hair growth is observed, mainly in mammals. They have a visible part, it is called the core, and the part hidden inside the skin is the hair bulb (in another it is also called the root). The bulb is in a kind of “bag” called the follicle.

Did you know that the shape of the follicle directly depends what type of strands decorates a man's head? From a follicle of a round form smooth strands grow, from an oval - wavy, and from a kidney-shaped - curly.

Each follicle has its own life cycle. This is a completely autonomous system that gives development and growth of hair.
Hair is able to absorb moisture and are conductors of electricity.

The figure clearly shows the structure of the scalp, and the location in it of the hair follicle, blood vessels, sebaceous and sweat glands, etc.
Did you know that when a child is born, a child already has a certain number of follicles? How many of them will get from birth to man - nature itself decides. To increase their number during life is impossible.
How curls grow
Individual color, number of follicles, structural features and growth intensity of a person’s strands are due to genetic factors. Influencing their structure dramatically is almost impossible.
That is why you should not blindly rely on advertising of cosmetic products that promise to turn weak, thin strands miraculously into chic hair. The maximum that hair products can do is to provide enhanced nutrition hair follicle, and as a result, get healthier and stronger curls. But no procedure will make the number of hairs on your head more than it is laid by nature.
The growth of strands is a continuous process, but during the day it proceeds a little faster than at night. Also, the curls are extended more intensively in spring and autumn, and in winter and summer their growth slows down a bit.

Hair growth is a cyclical process that continues throughout a person’s life. Life stages of a hair are divided into three cycles:
- anagen (active growth phase),
- catagen (intermediate period),
- telogen (rest and fallout phase).
Therefore, hair loss throughout a person’s life is a normal process. In a healthy person, it passes almost unnoticed, since about 85% of the whole head of hair is in the anagen stage, 14% is in the intermediate phase, and only 1% is in the telogen stage.
On average, the increase in the length of strands per month is: in children - 13 mm, in young and middle-aged people - 15 mm, and in the elderly - 11 mm.
Learn more about what hair is from the video.
Each person, like his hair - is unique. Therefore, it is not necessary to try to remake what is laid by nature itself. From gentle soft strands you will never make a thick and tough hair. Better take care of proper care and nutrition of your hair, and you will see that in fact they are beautiful, regardless of their type and thickness.
External structure

The photo clearly shows the structure of the hair shaft
The visible part of our hair consists of three layers:
- The inner part of the rod is the core, it contains non-horned cells.
Note! The core is not contained in every hair. For example, in the "light gun" it is not!
- Cortex - Cortex. It consists of an elongated cell shape and makes up 90% of the mass of the hair. The composition of the fat grease includes a natural antiseptic, which additionally protects the cortical layer of the rod from the penetration of various infections.
Interesting to know! It is in this part of the rod contains melanin, which determines the color of our hairstyle.
- Outer layer - cuticle. In appearance it resembles scales such as tiles or cones, where each successive particle coincides in area with the one in front.
Such particles are located in 7-9 layers, which are mounted with a specific composition. Scales grow from root to tip, and it is this layer that glitters. An important function of the cuticle is to protect the inner layers of the strands from external influences.

If all the scales reflect the light and lie flat, that is, there is a shine visible to the eye - the hair is healthy!
The condition of the scalp depends on the state of the internal environment of the body. For example, during various diseases, the condition of the locks may sharply worsen. This happens because the supply of a sufficient amount of vitamins and nutrients to their outer and inner layers stops.
Internal structure
Each hair has its place - its own follicle, in other words, it is a matrix for cell growth. The structure of the hair root is a kind of bag, which is located in the follicle (recess, pore). This very bag down slightly expands, forming a hair follicle.

Scheme of the hair structure (its internal structure)
But the sebaceous, sweat glands and blood vessels are suitable for the bulb - they all ensure the removal of waste products and deliver nutrition to the hair. On the inner side of the follicle is the hair papilla, consisting of connective and nervous tissue and the finest vessels. And while the root is alive, located in the scalp - hair grows in length.
Like any other body, hair performs its functions:
- Protective. During exposure to ultraviolet rays, it is due to curls that the skin does not get direct sunlight.
- Tactile function. A huge number of nerve endings makes the scalp sensitive to changes in the position of the curls.
- Thermostatically controlled. Even before they invented warm clothes, people protected their hair from hypothermia and colds. Such a structure of the root hair is not at all accidental. For the normal functioning of the brain vegetation on the head keeps a comfortable temperature. And when cooled, the straightening muscles cause the hair to rise, which prevents its own heat from leaving the skin.

The skin of the head plays a significant role in human life
Stages of hair development
There are three stages of hair development:
- Anagen. This stage lasts 2-4 years (in some cases up to 5-6 years), during this period the most active work of the follicle is observed, since there is an intensive growth of cells and their division. And it is due to this hair that grows continuously. In a healthy person, approximately 85-90% of the locks are of this age.
- Catagen. This period lasts only 8-20 days, in which the activity of the follicle is significantly reduced. However, the cells of the papilla are still functioning, albeit weakly. By the end of this phase, the bulb from the feeding papilla is rejected. Approximately 1% of the strands should be in this stage.
- Telogen. This phase lasts for 30-100 days. In the hair root, during this time, the cells no longer divide, and the bulb leaves its place, naturally with the stem. Further on the vacant space begins the anagen stage already in the new follicle.

Stage of follicle growth
Density and quantity
Interesting, but true! The structure of the scalp is to some extent determined by their color.
For example, it is noted that the thickness of the rod:
- at blondes = 50mk,
- have brunetov = 75mk
- at red = 100mk.

Natural hair color determines their thickness.
The number of follicles is laid, rather, at the genetic level. Thus, the density of rods on the head can reach different people in different ways, from about 100 to 150 thousand.
As for the shape of the curls, this is determined by the location of the follicle relative to the head. Because strands can be wavy, straight or curly.

This is how follicles are located in various forms of curls
At last
Truly, knowledge is power! And in this material you were able to find out for yourself a lot of useful information that will certainly help orient yourself in competent care for the scalp and hair. After all, the price of proper organization of life and hair care is your health and your beauty.
Do not forget to eat vitamins and breathe fresh air more often.
More visual information on this topic is in the video in this article, do not miss!
The structure of human hair. Phases of hair growth on the head. Hair structure improvement
Well-groomed hair is the dream of any woman. Spending a lot of time and effort on different styling, curling and coloring, many girls forget that the key to a beautiful hairstyle is a healthy head of hair. To make it so, you need to know what the structure of the hair, what is its life cycle, the causes of pathological changes and how to eliminate them.
From the roots to the tips

Each hair includes several elements. Its visible part is the rod, which consists of non-living cells filled with keratin. In the thickness of the scalp (at a depth of about 2.5 mm) is that part of the hair, which determines its appearance - the root. It consists of many living cells that continuously divide. This process ensures hair growth. Cell division is impossible without the participation of tissues located near the root. Together they form a hair follicle, from which the nerve ending departs. The structure of the hair on the head is such that damage to this end leads to the complete death of the root without the possibility of its further recovery. The work of the sebaceous glands, located next to the follicles, has a great influence on the beauty of the hair. If they are excessively large, then the scalp becomes oily. Underdevelopment of the sebaceous glands leads to its dryness. Also in the thicker skin next to each hair is a muscle that ensures its recovery.
The influence of growth phases on the hair

Most of the hair falls out during the period of its telogenic stage. Some, however, persist until the very beginning of the anogenic phase. At the same time they fall out at the moment when the newly emerging hair shaft pushes the old one.
The phases of growth, as well as the structure of the human hair, determine the appearance of the hairstyle. Long curls, for example, the easiest way to grow at a young age. This is due to the fact that each hair has about 25 cycles of life, with each of which it grows less and becomes thinner. In addition, after 30 years, hair growth gradually slows down. Until this age, they grow by about 1.5 cm per month.
Causes of hair problems
There are a number of reasons that can cause slower growth, hair loss, adversely affect their appearance. These include:
- Diseases of the endocrine system, disruptions in the hormonal background and problems in the field of gynecology.
- Diseases of the digestive tract, impaired liver and kidney function.
- Take some medicines.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Heavy physical exertion and stress, after which the hair begins to fall out not immediately, but after 2-3 months.
- Improper hair care, the negative impact of styling products, paints.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight on the hair, sudden changes in temperature. Excessive overheating of the scalp or extreme cold also adversely affect the health of the locks.
Thus, beautiful hair is a sign of a healthy and efficient body. Dull and brittle curls are often a reflection of various chronic diseases and pathological conditions that must be addressed first.

Vitamins for a beautiful haircut
Very often, the structure of the human hair and the duration of the anogenic phase change for the worse due to the lack of vitamins and microelements. Hair becomes dry, brittle, devoid of shine. In this case, you should review the diet or try to fill the lack of vitamins with special additives. When choosing them you need to pay attention to the presence of the following components.
- Vitamins of group B. Their deficiency in the first place leads to the loss of hair shine and their dryness. And vitamin B3, for example, is responsible for the normal amount of coloring pigment. Its deficiency in the body manifests itself early gray hair.
- Vitamin A. Under its influence the damaged structure of the hair is restored, it becomes elastic.
- Vitamin C is an excellent hair growth stimulant.
- Vitamin E is one of the sources of nutrition for hair follicles. Especially recommended to owners of long hair.
- Zinc prevents the formation of excess sebum, normalizes oily skin of the scalp.
- Iron and calcium are needed to prevent premature hair loss.
- Silicon is involved in the formation of collagen and elastin, due to which the hair becomes elastic.

Hair care
Improving the structure of the hair is possible and subject to some simple rules of care.
- Regular washing of hair as it gets dirty.
- Compliance with the optimum temperature. You should not wear too warm hats, in which the scalp is constantly sweating. At the same time, being without a headgear at a temperature below 3 degrees for 10 minutes leads to a significant reduction in the anogenic stage of the hair life cycle.
- It is necessary to avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, since the structure of the hair on the head changes for the worse. In summer, especially while relaxing on the beach, it is better to wear a Panama.
- One of the conditions for the possession of luxurious hair - sparing methods of their styling. Daily curling, blow-drying, dyeing - all this leads to problems with curls.

Qualified help
The structure of the hair is to some extent an indicator of the state of the body as a whole. Therefore, if on condition of a diet that provides the body with the necessary vitamins and trace elements, and proper hair care, they continue to fall out and look lifeless, you should contact a trichologist. You should not try to cope with the problem yourself, because it can be a symptom of a chronic disease. The trichologist will help deal with the causes of pathology and, if necessary, refer you to other doctors for consultation.



