In the lower part of the follicle there is a rather large formation - a papilla formed mainly from connective tissue and a grid of blood vessels. The papilla controls the condition and growth of the hair - if the papilla dies, the hair dies, if the papilla has survived, a new one grows in the place of the lost hair. The cells of the hair papilla, perceiving the influence of bone morphogenetic protein 6 secreted by the tissue “niche” of the follicle, acquire the ability to induce the formation of a new follicle, triggering the differentiation of epidermal stem cells.
Hair Muscle Edit
Just below the sebaceous gland to the follicle is attached muscle, lifting the hair (musculus arrector pili) consisting of smooth muscles. Under the influence of certain psychological factors, such as rage or arousal, as well as in the cold, this muscle lifts the hair, which is why the expression “hair rose on end”.
Other structures Edit
Other components of the hair follicle are the sebaceous (usually 2-3) and sweat glands, which form a protective film on the skin surface.
There are three stages of follicle development: anagen (growth period), catagen (transition from one stage to another) and telogen (rest period). Presumably the hair cycle begins with catagen. At this stage, atrophy of the papilla begins, as a result, cell division of the hair bulb stops and they are subjected to keratinization. The catagen is followed by a short telogen phase. Most loose hair is telogen. The telogen stage passes into the anagen stage, which is divided into 6 periods of development. After completion of the anagen a new hair cycle begins.
Normally, in a healthy person, 80-90% of the hair is in the anagen stage, 10-15% in the telogen stage and 1-2% in the catagen stage.
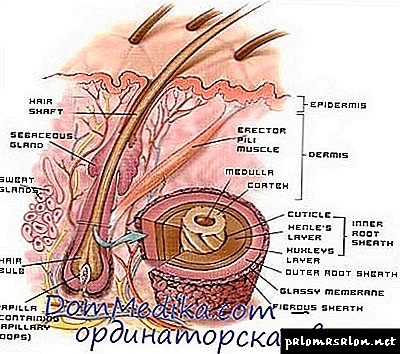
Hair structure
Each hair on the human body consists of two main parts:
- The hair shaft. This is the visible part that rises above the skin.
- Hair root This is the name of the invisible part of a hair hidden inside a special skin cavity - the hair follicle.
The hair follicle itself, in combination with nearby structures, forms the hair follicle.
The cycle of the human hair follicle. Phases
Human hair follicle cycle it is accepted to divide into phases:
— telogen - the resting phase of the hair: the hair is retained in the sac due to intercellular compounds, but the metabolic activity in the follicle is minimal, the follicle will pass into the next phase (anagen) either spontaneously or as a result of removal of the telogen hair from it,
— anagen - phase of maximum metabolic activity, divided into proanagen and methanagen:
a) sub-phase "proanagen»:
Stage I - activation of RNA synthesis in the papilla cells, the beginning of the active division of germ cells at the base of the sac,
Stage II - the growth of the hair follicle in depth,
Stage III - the formation of a cone of the inner root vagina as a result of the proliferation of matrix cells (when the follicle reaches its maximum length),
Stage IV - the hair is still inside the root sheath, a keratogenic zone forms below the mouth of the sebaceous gland, dendrites appear in melanocytes - a sign of increased metabolism and the onset of melanin production,
Stage V - the tip of the hair passes through the cone of the inner root of the vagina,
b) sub-phase "methanagen": Appearance of hair on the skin surface,
— catagen - reduction and phasing mitotic activity of matrix resorption dendrites of melanocytes, the terminal part of the hair loses pigment and keratiniziruetsya, shortening, thickening and wrinkling of the connective tissue of the vagina and glassy shell promoting hair papilla closer to the surface, the disintegration of the internal root sheath, the bulb of the hair is surrounded by a capsule of partially cornified cells, and is retained due to the connections of these cells with non-cornified cells at the base of the sac, dermal The papilla is strongly tightened in the direction of the epidermis, the expression of E- and P-cadherins in the epithelial severity of the regressing follicle is enhanced.
On human body About 85-90% of hair is in the anagen phase, about 1% in the catagen phase, 9-14% in the telogen phase. Phase duration: anagen - from 2 to 5 years (which is easy to remember, like 1000 days), catagen - 2-3 weeks (15-20 days), telogen - 100 days. Thus, the ratio of anagen and telogen hair is 9: 1. The size of the tslogeic follicle is 3-4 times smaller than that of the anagen.
At some point between the end catagen and the beginning of a new anagen phase, the hair shaft is actively removed from the follicle, after which the mechanisms of stimulating the growth of a new hair are activated. The mechanisms that ensure this active hair loss are not yet known. To denote this phase of active deposition, the term "exogen" was proposed.
How to grow hair?
Hair - derivatives of the epidermis, the outer shell of which is formed by keratin scales, consistently overlapping each other. The visible part of the hair is called the core, and the inner, under the thickness of the skin, the root or the bulb. The root of a hair is surrounded by a peculiar bag - a hair follicle, the shape of which directly determines the type of hair: curly locks grow from a kidney-shaped follicle, slightly curly (wavy) - from oval, and straight lines - from rounded.
Each hair consists of three layers. The first (outer), called the hair cuticle, performs a protective function. The second (middle) is the cortex. It consists of elongated dead cells, giving the hair elasticity and strength. In addition, the pigment (melanin) is concentrated in the cortex, which determines the natural color of the hair. In the very center of the hair is a medulla (medulla), consisting of several rows of keratin cells and air cavities. It is believed that through this layer the nutrition of the cortex and cuticle is provided - this, in fact, can be attributed to the change in the condition of hair in diseases associated with a lack of nutrients in the body. Hair growth occurs due to the division of undifferentiated (immature) cells of the hair bulb, which have a high mitotic activity. This process is subject to certain biological laws and includes several phases, which we consider below.
Anagen (growth phase)
Anagen - a period of active hair growth, which lasts an average of 2 to 6 years. With age, this phase shortens considerably (in older people, it usually lasts no more than 3 years). Anagen is divided into several stages:
- The cells of the hair bulb begin to increase in size, there is an active synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- The hair bulb penetrates deep into the dermis, forming a connective tissue sheath - a hair bag. In the lower part of the follicle extends the hair papilla - education, consisting mainly of connective tissue, small blood vessels and nerve processes. The cells of the bulb, actively multiplying, become part of the hair and ensure its growth.
- Then the active division of differentiated cells continues, and the follicle at this point reaches its maximum length (it is 3 times its length in the resting stage). The papilla becomes fully formed. The melanocytic epidermal cells located among the cells of the follicle matrix near the papilla form melanin granules (they are responsible for the hair color). The outer sheath of the follicle takes the form of a cone, expanding from above. Subsequently, epithelial cells, when subjected to keratinization, will turn into brain and cortical substances.
- At this stage, the melanocyte cells begin to produce pigment, and the hair, which is already fully formed, does not go beyond the limits of the follicle, which continues to expand.
- The formed hair shaft grows to the upper boundary of the epidermal layer, the bulb (hair root) gradually acquires, so to speak, a complete form (it can be elliptical or symmetrically rounded).
- At the last stage of the anagen, the hair shaft begins to rise above the surface of the skin, followed by a transition phase. The duration of the stage of active hair growth is different for each person (it depends on many factors, including genetic predisposition).
Perhaps the most illustrative example of the anagen phase is the head of a newborn baby. At first, it is covered with a barely noticeable down, and after a while, intermediate hair begins to grow on it, and then terminal (hard and pigmented) hair, which after a few years turns into a full-bodied hair.
Catagen (intermediate phase)
After the active growth phase, a hair begins a period of rest, during which the hair shaft no longer grows. Various biological processes can occur in it, but its length does not increase. This is due to the fact that at this stage the supply of nutrients to the follicle stops, and the follicle begins to shrink gradually, significantly decreasing in size. At the same time, melanin ceases to be synthesized. Catagen is considered the shortest phase, since its duration is not more than 2-3 weeks.
Telogen (resting phase)
The intermediate phase of hair growth ends with a stage of rest (rest), which is conventionally subdivided into early and late telogen. Conventionally, because some experts refer the early phase of rest to the previous stage (intermediate), and the late telogen is separated into a separate cycle, called an exogenous one. But we will consider the generally accepted classification:
- Early telogen is a stage in the life cycle of a hair where its bulb becomes inactive. During this period, the dermal papilla enters a state of rest, and the nutrition of the hair root completely stops. At the same time, the hair shaft can still remain attached to the lower part of the follicle and receive signals through the fibers in the extracellular mass. It is noteworthy that the mechanical removal of hair in the telogen phase necessarily entails the onset of the stage of active growth of a new hair. Every day, a person loses up to 100 telogen hairs (in people over the age of 50, loss of 150–200 hairs is considered the norm). The duration of this period is on average 2-3 months.
- Late telogen - the last phase, during which the natural death of the hair and its loss occurs. The hair sac surrounding the bulb is dormant, and the hair itself is retained only by the skin, so it can easily fall out with any effect. Usually such a phenomenon occurs when a new, only emerging hair begins to actively push the old one. Next comes the first stage of the hair cycle - anagen. The main danger of the late dormancy phase lies in the fact that during it the root cells may die (for various reasons), and the follicles therefore lose the ability to produce new hairs (thus alopecia develops).
It should be noted that in healthy people, usually about 85–90% of all hair is at the stage of active growth, 1–2% - in the intermediate phase, and 10–15% - at rest. According to studies in trichology, mass hair loss (alopecia) corresponds to a change in the above ratio. Simply put, the hair begins to thin intensively when the percentage of hairs in the anagen and catagen phases decreases, while the percentage of telogen hair, on the contrary, increases. In this case, it is often possible to observe that each new generation of hairs differs in characteristics (thickness, color, and potential length) from the previous one (they become thinner, weaker, and faded).
If, in violation of the hair growth phases, no action is taken, this process can become pathological in nature, and then the hair follicles will atrophy and will not be able to produce new hairs. And this, in turn, threatens with the appearance of pronounced bald patches, which will increase in size over time. If we talk about the treatment of alopecia, then its essence lies primarily in normalizing the balance between the phases of the life cycle of the hair and eliminating the factors that caused such disorders. Conduct therapy should be under the supervision of a specialist, as soon as he can carry out a competent diagnosis and select the appropriate treatment program.
What factors can affect hair growth?
Hair growth can be influenced by various factors, but especially the following ones should be highlighted:
- Times of Day. It has long been proven that the length of hair rods in the morning and in the afternoon increases much faster than in the evening and at night. It is for this reason that most cosmetic procedures aimed at accelerating the growth of curls, it is recommended to do at bedtime.
- Season. The process of hair growth can be compared with the life cycle of plants, which they go through for a year. The most active curls grow in spring and summer, but in cold seasons their rate of growth decreases significantly.
- Hair type. It is known that straight hair grows much faster than wavy hair (this is probably due to the structural features of the follicles and the structure of the hairs themselves).
- Heredity. An important factor that has a direct impact on the life cycle of hair. People whose immediate family started losing their hair early, are more likely to face the same problem.
In addition, the processes of formation and growth of hair have a close relationship with the general state of the body, nutrition and lifestyle of a person, and even with his race. So, among the representatives of the Mongoloid race, the average lifespan of a hair is much longer than that of Europeans and Asians, but the latter can “boast” of the highest growth rate and strength of curls.
How to accelerate hair growth: general recommendations
To increase the growth rate of curls and improve their overall condition, you should heed the following tips:
- Of great importance is competent care. It is desirable to exclude or at least minimize the use of high-temperature devices and chemical agents for dyeing and curling hair.
- You should not save on cosmetics for curls, it is better to purchase quality products containing the minimum number of chemical components.
- To maintain curls in a healthy state, you need to provide them with good nutrition from the inside. This can be done by including in your daily diet a sufficient amount of foods rich in vitamins and minerals, or by taking vitamin complexes (courses).
- To activate hair growth, it is useful to systematically perform a head massage. It helps to improve blood circulation and accelerate the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the follicles. Massage can be done with a special brush or just with your hands.
- In addition to the main care, it is recommended to regularly make masks from natural products that can accelerate hair growth - vegetable oils, herbal extracts and decoctions, vitamins.
Having an idea of how hair grows and through which phases it goes through, starting from its inception to the moment of natural death, you can try to at least partially control this process. To do this, follow the simple rules of care for hair, constantly protect it from all sorts of negative factors and promptly carry out prevention and treatment of diseases that contribute to the violation of the life cycle of the hair.
Anatomy of a greasy hair and nutrition of glands
Each hair consists of two main elements: the core and the root.
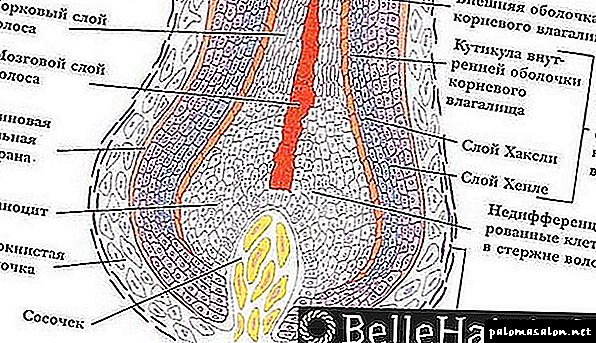
Hair root is a kind of mini-organ. It depends on the entire life cycle of the hair. The size of the follicle may vary depending on the stage of its growth.
At the base of the follicle is a small papilla. This element consists of many capillaries, lymphatic vessels and connective tissue. It ensures the saturation of the follicle with blood and beneficial microelements.
The papilla is surrounded by a bulb in the form of a cap. This element provides hair growth. Close to the bulb are the sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as the involuntary muscle responsible for the extension and contraction of the follicle.
In the follicle there are also special cells - melanocytes. They produce the pigment melanin, which forms the hair color. With age, the activity of melanocytes slows down, and the medullary layer is filled with a large number of air bubbles. This leads to graying hair.
The rod is a part of the hair located on the surface of the scalp. The core consists of 3 layers:
- The medullar layer is a medulla filled with air atoms.
- The cortical layer (or main substance) is a dense layer consisting of a variety of keratin fibers.
- The outer layer (cuticle) - a thin shell that protects the hair from mechanical and thermal damage.

The life cycle of the hair and the bulb
In its development, the hair follicle goes through 3 main stages:
- Anagen - the period of the greatest activity of the follicle. At this stage, there is a constant cell division and rapid hair growth. In addition, melanin is rapidly formed during the anagen period. This stage of growth can last from 2 to 5 years, after which the hair moves to the next phase.
- Catagen is an intermediate phase of growth that can last less than a month. During this period, the process of cell division slows down, after which the bulb is rejected from the sac.
- Telogen - the final phase in the life cycle of the hair. At this stage, the process of cell division stops completely, the follicle dies and falls out together with the stem.
Diseases of all types of follicles on the head: inflammation and destruction
Follicle thinning is a disorder associated with the deformation of the sac. In most cases, thinning occurs under the influence of stress. With strong emotional upheavals, the involuntary muscle contracts and squeezes the bulb, which leads to its deformation and gradual death. In addition, thinning can occur under the influence of certain hormones. With a high content in the body dihydrotestosterone, the follicle shrinks and gradually becomes thinner.
 The disease must be treated in order not to lose all hair.
The disease must be treated in order not to lose all hair.
Regenerating masks and other drugs will help sleeping follicles.
Follicle atrophy - a disease that develops on the background of the deformation of the bulb. Untimely treatment of thinned hair leads to the fact that they gradually stop growing or grow thin and colorless. Treatment of the disease includes a set of procedures aimed at strengthening the hair roots and slowing the process of their death. In case of atrophy, the trichologist prescribes stimulating preparations, restoring masks and head massage.
Sleeping hair follicles - a disease that is characterized by the cessation of vital activity of the root. The sleeping follicle, as a rule, does not fall out. It can be detected by microscopic examination of the scalp. However, sleeping onion ceases to produce new hair. As a result, pleshes are formed in a person. This disease requires long-term treatment and observation with the trichologist.
Description of the structure and stages of follicle development
A follicle is a complex of several mini-organs surrounding the hair root. You can see its enlarged sectional view in the picture. The follicles are located in the dermal layer and are fed by small blood vessels suitable for them.
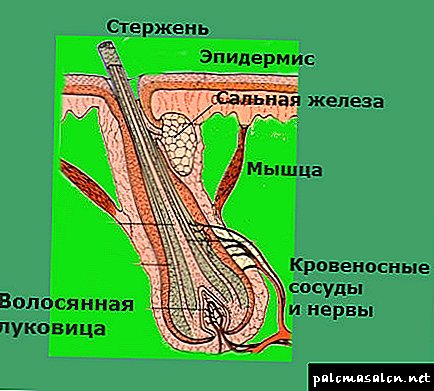
The structure of the hair follicle - a diagram in section
What is the follicle
The structure of this body is quite simple:
- The hair bulb (dermal papilla) is a connective tissue formation located in the lower part of the follicle, containing blood vessels and nerve endings through which oxygen and nutrition are supplied. They provide constant cell division of the bulb, responsible for the growth and condition of the hair.
For reference. If the hair is pulled out by the root, but the dermal papilla remains in place, a new hair will grow from it.
- The follicular funnel is a depression in the epidermis where the hair comes to the surface of the skin. It opens the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
- The sebaceous and sweat glands that make up the follicle are responsible for lubricating and moisturizing the hair, giving it flexibility, elasticity and shine, creating a protective film on the surface of the skin.
- The follicle root vagina is a three-layer “bag” in which the hair root is located. The cells of its inner layer are involved in the formation of the hair.
- The hair muscle located under the sebaceous glands, raises hair when exposed to cold or nervous excitement.
For reference. It is the contraction of the smooth muscles of this muscle that causes the sensations of which they say "the hair on the head moves."
Stages of development
Hair follicles constantly go through cyclic stages of rest and growth:
- Anagen is a growth stage, the duration of which is genetically determined and lasts an average of 2-4 years. In this stage, a healthy person is about 85% of the hair.
- A catagen lasting for 2-3 weeks and affecting about 1-2% of hair is a transitional stage, during which the nutrition of the cells is reduced, they cease to divide.
- Telogen - the resting stage of the follicle, lasting about three months, during which hair that ceases to grow falls out. After which the cycle repeats again.
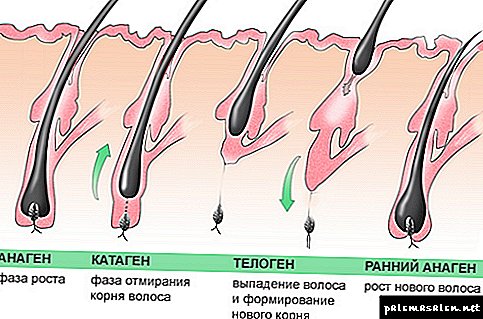
All stages of development
That is, the hair that remains on the brush after combing - those that have come to fall out and make room for new ones. But sometimes the telogen stage is delayed, the bulbs do not want to wake up and work, which leads to thinning of the hair.
How to wake up sleeping bulbs
Many hair problems are associated with malnutrition and follicle failure. And they often manage to cope with them using simple methods such as massage, nourishing masks, etc.
Council Before taking measures against hair loss, consult a trichologist.
The specialist will determine the cause of the problem and advise treatment. You may need more serious therapy.
If such a nuisance is only evident or you want to do prevention, the following instructions will help you maintain healthy hair.
- After washing your head, always perform a massage in soft circular motions.. The tips of the fingers should move from the temples to the occipital and central parts of the head.

Independent head massage
- Periodically make stimulating masks. Their main ingredients are onion juice, garlic and aloe, mustard powder for hair. To them, you can optionally add honey, egg yolk, oatmeal, as well as various cosmetic oils. After thorough mixing, the mixture is rubbed into the scalp and aged for 30-50 minutes, then rinsed with warm water.
- Use hair follicle growth activator, which is a part of special medical shampoos, lotions and balms.

Hair growth activator is available in different forms.
For reference. An excellent activator are burdock and castor oil. They are used by themselves or as part of nutritional masks. Their price in the pharmacy is very affordable.
Follicle structure:
Hair (dermal) papilla - connective tissue formation located in the lower part of the follicle and connecting it with the skin. The papilla contains nerve fibers and blood vessels, through which the constantly dividing cells of the bulb feed and oxygen. In shape, it resembles a candle flame. Its function is to control the condition and growth of hair. If the nipple dies, the hair also dies. But if at the death of the hair (for example, if it is torn out by the root) the papilla is preserved, then a new hair will grow.
Hair (follicular) funnel - funnel-shaped depression in the epidermis of the skin in the place where the hair root passes into the rod. Coming out of the funnel, the hair appears above the surface of the skin. The duct of one or several sebaceous glands opens into the hair funnel.
Hair muscle - muscle attached to the follicle a little deeper than the sebaceous gland, consisting of smooth muscles. The muscle passes at an acute angle towards the axis of the hair. Under certain circumstances (for example, with emotional arousal or in the cold), she raises her hair, which is why the expression “hair stood on end” went.
Root Vagina - the bag surrounding the hair root. It consists of three layers. The cells of the inner root vagina are involved in the formation and growth of hair.
Greasy (they are usually 2-3) and sweat glands are also components of the hair follicle. They form a protective film on the surface of the skin, and the secret of the sebaceous glands lubricates the hair, giving it elasticity, flexibility and shine.
Follicle structure
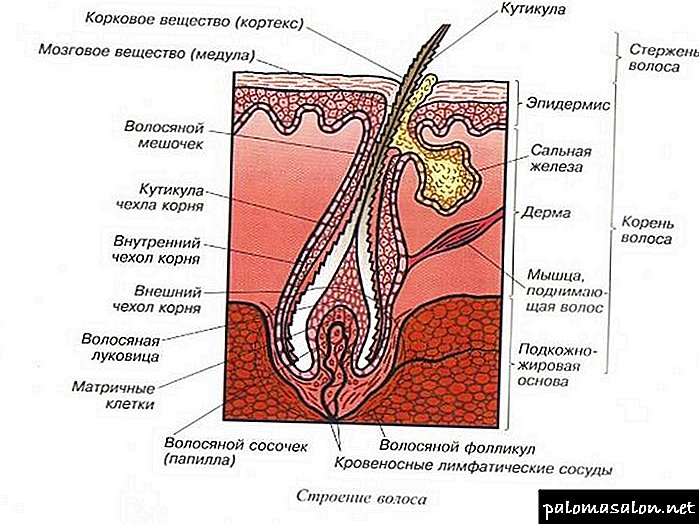
The hair follicle is also sometimes called the bulb. But this is the wrong definition. A follicle is essentially a basic structural entity that is responsible for producing hair, controlling its condition and growth. Inside it is an onion - this is the lower extended part of the hair root.
The hair follicle has a rather small size, but rather a complex structure. It contains:
- Hair papilla.
- Hair funnel.
- External root vagina.
- Keratogenic zone.
- Internal root sheath.
- Sebaceous and sweat glands.
- The muscle responsible for hair lifting.
- Blood vessels.
- A series of nerve endings.
Violation of the full activity of any of these structures can lead to hair loss or deterioration of its quality.
Muscle tissue
A muscle is attached to each hair follicle (except for bristly hair). It is localized slightly lower than the sebaceous gland. This structural unit consists of smooth muscles, it is responsible for lifting the hair. In particular, in case of emotional shock (for example, during a rage) or during a chill, this muscle lifts the hair, which can sometimes be seen with the naked eye. In addition, the reduction of smooth muscles contributes to the emptying of the sebaceous glands.
Causes of inflammation
In addition to those already listed, folliculitis of the scalp may occur for other reasons.
- Malnutrition, causing malfunction of all organs,
- Serious common diseases, such as anemia or diabetes,
- Contact with bacteria when visiting baths, saunas, swimming pools, using someone else's bath accessories,
Note. The risk of infection is especially great if there are wounds and scratches on the scalp.
- Long-term use of certain hormonal drugs, etc.
Forms of the disease and methods of treatment
Folliculitis, depending on the degree and depth of the lesion, is conditionally divided into three forms - light, moderate and severe.
- Ostiofolliculitis of the scalp is the lightest, superficial form of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of a small, about the size of a pinhead, an abscess that does not cause pain or other unpleasant sensations. After 3-4 days without any interference, it dries out, transforming into a crust, and falls off, leaving no trace.
- The folliculitis of moderate severity lasts longer - 5-7 days and is characterized by deeper inflammation, the abscess causes itching and pain, with time it is opened with the release of pus. In its place may remain small scars.
- In severe cases of the disease, the pus penetrates rather deeply, affecting the follicle, which even after opening the abscess and scar formation is no longer able to form the hair.
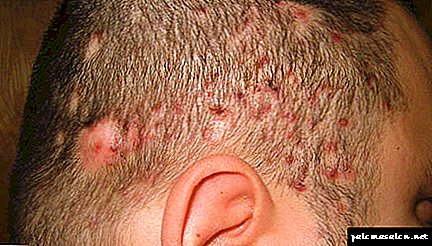
In the photo - severe folliculitis of the scalp
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease. Staphylococcus is destroyed with antibiotics, fungal infections with antifungal drugs. Diet and vitamins for hair compensate for the lack of nutrition, etc.
In this case, external treatment of the affected areas with aniline dyes is necessarily carried out, and if necessary, dissection of pustules with removal of pus and skin treatment with alcohol solutions to prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion

The health of our hair depends not only on proper care for them, but also on how well we generally care about our health.
Hair follicles, which are a kind of mini-factories for the production of hair, also need care, nutrition, hygiene, etc. The video in this article will tell you how not to let them grow old and stop functioning ahead of time.
Sebaceous and sweat glands
The sebaceous glands are responsible for producing a secret that enters the hair follicle. This substance lubricates the hair shaft, which is why the curls look elastic and shiny. In collaboration with sweat glands, they effectively cover the skin with a protective film that prevents the aggressive influence of various infectious agents. In addition, the secret secreted from such glands, provides reliable protection of curls from all sorts of aggressive environmental factors.
If the sebaceous glands work excessively, the hair quickly becomes greasy and untidy. And with insufficient functioning, hair shafts dry out and quickly break.
Stages of growth

On average, approximately one hundred thousand hair follicles are present on the skin of the human scalp (perhaps even more). At the same time from each can grow up to twenty to thirty hairs. Hair growth occurs through active reproduction of hair follicle cells - the matrix. They are located directly above the papilla, begin to mature and divide. These processes occur inside the follicle, but over time the cells move upward, solidify (undergo keratinization) and form the hair shaft.
Each hair passes alternately different stages of activity:
- Anagen Phase. At this stage, there is active and continuous hair growth. The cells of the matrix begin to actively divide, the papilla of the hair and the hair bag are forming. The follicle is actively supplied with blood. Due to this, the production of hair cells is particularly fast, they are gradually keratinized. High pressure and continuous division leads to the fact that the hair moves to the surface of the skin, the growth rate at the same time can reach 0.3-0.4 mm per day. The duration of anagen can vary from three to six years and depends on the individual characteristics of the person.
- Phase catagen. This period is considered transitional. At this time, the rate of division of the cells of the matrix is gradually reduced, wrinkling of the hair bulb is observed. At the same time, the papilla gradually atrophies, as a result of which the processes of feeding the hair are disturbed and the cells of the bulb begin to coarsen. This period may be delayed for two weeks.
- Phase telogen. This period is also called rest time. The process of cell renewal stops, the hair follicle easily detaches from the hair papilla and begins to move closer to the skin surface. Hair at the same time can easily fall out in response to the slightest tension (for example, when washing or combing). When the telogen phase comes to an end, the papilla begins to wake up, the follicle gradually reconnects with it. The processes of new hair growth are launched, which over time pushes its predecessor (if it does not fall out by itself). The anagen period begins again.
All hair follicles live their lives. Accordingly, at different times on the body are hair in different stages of development. But, it is necessary to recognize that most of them are actively growing - they are in the anagen phase.
If hair follicles are aggressively affected (ill), these growth phases may be disrupted. The result is baldness - alopecia. An experienced trichologist will help to determine its cause exactly and correct the problem.



